An Introductionary Guide to Change Management
What is Successful Change Management?
Introduction to Change Management
Sure we have all heard of Change Management, but what is it. Change Management is something everyone will have heard of and will experience in their career, either as a victim or leader.
In this article we will cover defining change management, why organisations want change, practical examples of Change.
Change Management: Change Management is the management of People, Processes, and Technology through a Change, caused by a shift in the internal or external forces on an organisation.
Within Change Management Change is not concerned with the daily changes in a business. Change also does not refer to an individual role or managerial change. Change, in Change Management, is a significant strategic change which impacts the organization. These change are significant measured by the impact on many/multiple employees and originate from the strategic direction and objectives.
“People like Changes but they don’t like to be Changed”
A Need for Change
Usually change began in an organisation by establishing a clear need for Change (Not to be confused with the first step in a Change Management Process). Establishing a c clear need for change is initated by a belief that change is required and necessary to remain competitive in the corporate environment, or whatever the guiding objective of the organisation is. Within the organisation every employee must understand that ‘you’ must change as an individual and on an individual level. Changes must occur in mindsets, behaviours and ways of working.
Resistance to Change
Resistance is where a lot of Organisations and Change Management is focused and therefore discussed. Resistance refers to the natural human resistance to change in the environment. In the Change Management context this is relevant to the impact this has on the Strategic Objectives of the Organisation. Companies seek to minimise dysfunction in an organsiation which results from resistance. The Change Management approach to resistance to change is heavily influences in the field of human psychology research. The Psychology of Change is interested in application of Group Theory Research which seeks to understand and naturally integrate the natural reactions of employees into the overall project change lifecycle. This is commonly seen in the Force Field Analysis.
Realising Benefits of Change
There are many benefits to Change Management. Change Management is ultimately about leading people through change. Some of the most visible elements of a Change project are improved communication, involvement, and training. However, it is important for an Organisational Change strategy to realise the full benefits of Change Efforts by leveraging all available Change Management Practices. An experienced Change Manager is responsible for the benefits and must nuture the environment required to implement effective Change Management.
Practical Change Management
These examples help present the clear rationale and approach for required organizational change management capability.
1. Financial Crisis Causes a Strategic Change for Major Bank:
Every organisation is reactive the balance of Internal and External Forces which impact upon it. Within the Banking Industry the public reaction to banking and monetary spending impact the required position of a Bank in the market. When a significant change is required, as needed in response to a Financial Crisis, banks change direction.
2. Compensation Structure Change in an Organisation
3. Organisational Structure to an Engineering Firm.
Types of Change:

Not only do we want to understand these Types of Changes but also appreciate and recognise these change in their practical explanations.
1. Restructuring – A common type of Change which involves restructuring Organisational Structure. For example a company may shift from a function focus to product focus. In the function focus the organisation will be function derived, Marketing-> Product Line, Production-> Product Line, Sales-> Product Line. In the product oriented organisation, Product Line -> Marketing, Sales, Product, Product Line2 -> Marketing, Sales, Product.
2. Reengineering – All companies have processes. A process is a line of actions which the company carries out as part of its operation. Processes can handle data, object, or people, which are input into systems and output. Reengineering the business systems is considered Reengineering.
3. Mergers and Acquisitions – M&A is a commonly publicised changes in identity of a company as a result of two or more companies changing ownership.
4. Strategic Change – Change in priority, direction and purpose of an Organisation. This is due to a resulting shift in the balance of internal and external forces on the organisation. A strategic change asks the ultimate questions of “Why does this organisation exist”
5. Cultural Change. Change the way people think and understand the purpose of their work.
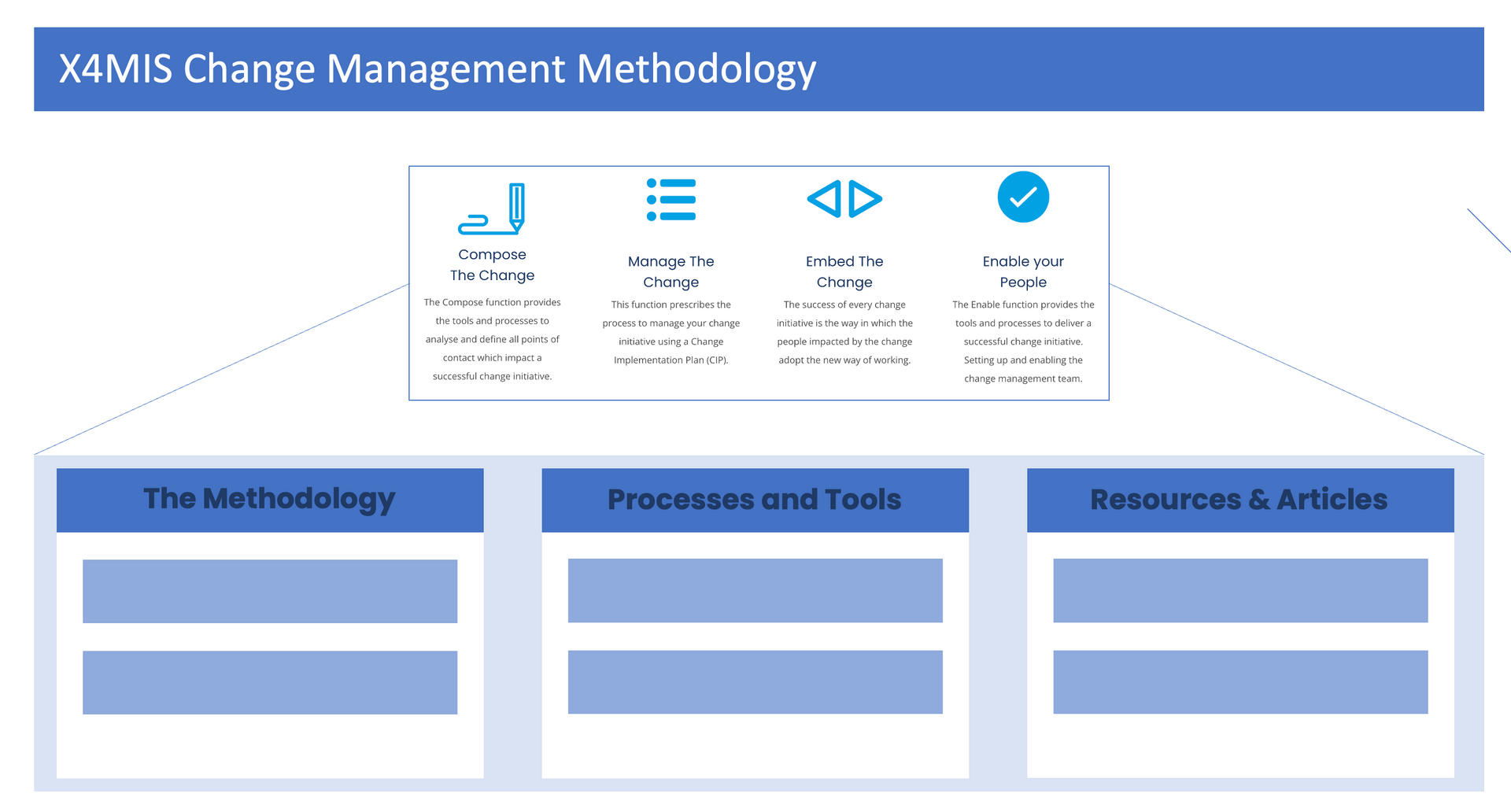
Compose the Change
Browse by Categories

Free On-Line Change Management Methodology that enables individuals and organisations, especially those previously without access to effective change management programmes, to deliver more effective community and country programmes which improve prosperity and save lives.
QUICKLINKS
TRAINING LINKS
LATEST POSTS




